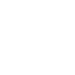7. Accessing and Submitting Metadata and Data¶
Contents
The Metacat repository can be accessed and updated using a number of tools, including:
- the Registry, Metacat’s optional Web interface
- user-created HTML forms
- Metacat’s EarthGrid API
- existing clients, such as KNB’s Morpho application, designed to help scientists create, edit, and manage metadata
- user-created desktop clients that take advantage of Metacat’s Java API.
In this section, we will look at how to take advantage of these tools to customize Metacat for your user-base.
7.1. A Brief Note about How Information is Stored¶
Metacat stores XML files as a hierarchy of nodes, where each node is stored as records in database tables. Because many XML data schemas are broken up into multiple DTDs requiring multiple XML files that are related but stored separately in the system, the system uses “packages” to link related but separate documents. Packaged documents contain information that shows how they are related to eachother, essentially stating that file A has a relationship to file B, etc. A package file also allows users to link metadata files to the data files they describe. For more information about the structure of data packages and how XML documents and data are stored in Metacat, please see the developer’s documentation.
7.2. Using the Registry¶
Metacat’s optional Registry provides a simple Web-based interface for creating, editing, and submitting metadata to the Metacat repository (screenshot below). The interface includes help documentation, and can be customized using Metacat’s configuration settings. The Registry also includes an administrative interface for managing LDAP user accounts, which is useful if you are using LDAP as your Metacat authentication system. Note that you must be running your own LDAP server if you wish to use the LDAP Web interface. If you do not have your own LDAP server, you can create and manage new accounts on the KNB website (http://knb.ecoinformatics.org/). Please note that at this time, the Registry interface has only been tested on Linux systems.
An example installation of the Register’s web interface. Customize the displayed and required modules with the Skins Configuration settings.
You can customize which modules (e.g., “Name of Submitter” or “Temporal Coverage of Data”) are displayed and which are required using the Skins Configuration settings
7.2.1. Installing the Registry¶
In order to install and run the Registry, you must have Metacat installed and Tomcat must be running behind an Apache Web server (see previous sections for information about installing and configuring Apache to run with Tomcat).
To install and run the Registry:
- Install the required system libraries using Ubuntu/Debian (instructions Red Hat in sidebar)
Install the libraries
sudo apt-get install ant libappconfig-perl libxml-libxml-perl \ libxml-libxslt-perl libtemplate-perl libcgi-session-perl \ build-essential libnet-ldap-perl libterm-readkey-perl \ libxml-dom-perl libsoap-lite-perl -yInstall two more package using cpan
sudo cpan -i Digest::SHA1 sudo cpan -i Config::Properties sudo cpan -i Scalar::Util sudo cpan -i Captcha:reCAPTCHA sudo cpan -i DateTime sudo cpan -i Crypt::JWT sudo cpan -i Crypt::X509
- Double-check that Metacat’s temporary folder, application.tempDir, is writable by the apache user, usually www-data or apache.
- Make sure that the following scripts (found in
<tomcat-home>/webapps/metacat/cgi-bin) are executable: register-dataset.cgi and ldapweb.cgi.
sudo chmod +x <tomcat-home>/webapps/metacat/cgi-bin/*.cgi
Ensure apache CGI module is enabled
sudo a2enmod cgid
Restart Apache.
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
- Visit the resulting URL:
http://<your_context_url>/cgi-bin/register-dataset.cgi?cfg=default
Where
<your_context_url>is the URL of the server hosting the Metacat followed by the name of the WAR file (i.e., the application context) that you installed. For instance, the context URL for the KNB Metacat is: http://knb.ecoinformatics.org/knb.
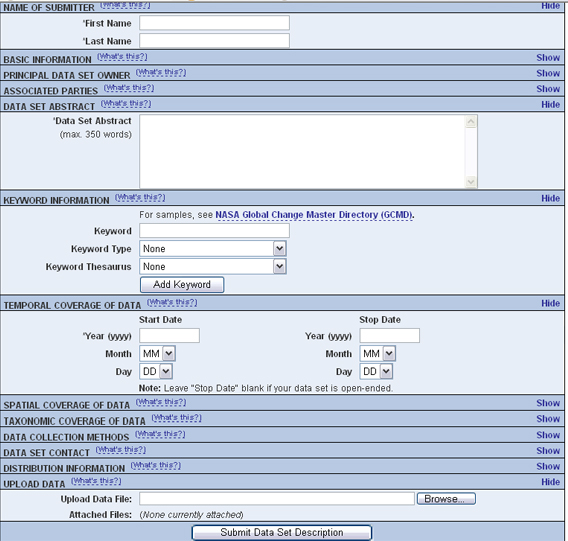
If everything worked correctly, the registry home page will open (see figure).
An example of the Registry home page (with the default skin).
7.2.2. Customizing the Registry¶
Before using the registry, you may wish to customize the interface using the Skins Configuration settings. If you are using the default skin, you must disable the ‘show site list’ setting before you can submit the form without errors. You may also wish to remove (or modify) the list of NCEAS-specific projects that appear in the default registry. To remove these form fields, open Metacat’s administrative interface (http://<your.context.url>/metacat/admin) and select the Skins Specific Properties Configuration option. On the skins configuration page, uncheck the boxes beside any form elements that you do not wish to appear in the registry.
Once you have saved your changes, you must restart Tomcat for them to come
into effect. To restart Tomcat, type: sudo /etc/init.d/tomcat7 restart or an
equivalent command appropriate to your operating system.
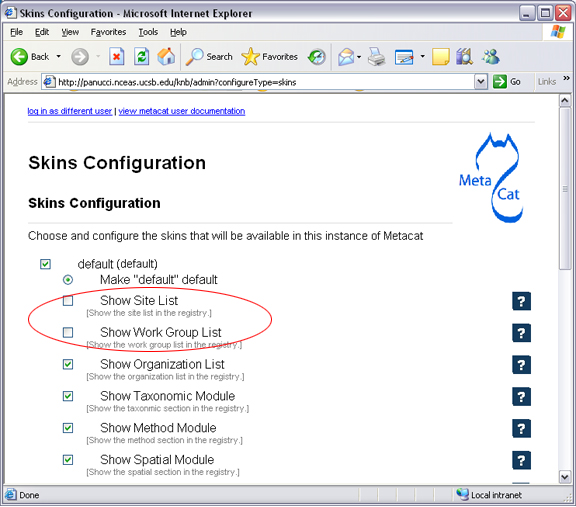
Uncheck the box beside any setting to remove it from the Registry form. In the example, the “Show Site List” and “Show Work Group” form fields, corresponding to the “Station Name” and “NCEAS Project” drop-down lists in the registry form, have been removed.
7.2.3. LDAP account management¶
If you intend to use Metacat’s built-in LDAP account management feature, you will need public and private keys for the reCaptcha widget.
1. Get private and public recaptcha keys from Google using your Google account: https://www.google.com/recaptcha/admin/create
- Configure Metacat to use those keys in the metacat.properties file:
ldap.recaptcha.publickey=<your public key> ldap.recaptcha.privatekey=<your private key>
- Restart Tomcat
7.3. Using HTML Forms (the HTTP Interface)¶
Metacat’s HTTP interface supports Get and Post requests and a variety of actions (Table 4.1) that facilitate information retrieval and storage. HTTP requests can be sent from any client application that communicates using the Web’s HTTP protocol.
- Supported Actions (API)
- Logging in
- Inserting, Updating, and Deleting XML and Data Documents
- Searching Metacat
- Paged Query Return
- Reading Data and Metadata
7.3.1. Supported Actions¶
Metacat supports get and post requests as well as actions for writing, querying, and reading stored XML. In addition, the HTTP interface includes functions for validating and transforming XML documents (see table).
Note that if Replication is enabled, Metacat recognizes several additional actions, included in Table 4.2. For more information about replication, please see Replication.
| Action | Description and Parameters |
|---|---|
| delete | Delete the specified document from the database. For an example, please see Inserting, Updating, and Deleting XML and Data Documents.
|
| export | Export a data package in a zip file.
|
| getaccesscontrol | Get the access control list (ACL) for the specified document.
|
| getalldocids | Retrieve a list of all docids registered with the system.
|
| getdataguide DEPRECATED Use getdtdschema instead | Read a data guide for the specified document type
|
| getdoctypes | Get all doctypes currently available in the Metacat Catalog System. No parameters. |
| getdtdschema | Read the DTD or XMLSchema file for the specified doctype.
|
| getlastdocid | Get the latest docid with revision number used by scope.
|
| getlog | Get the latest docid with revision number used by user.
|
| getloggedinuserinfo | Get user info for the currently logged in user. No parameters. |
| getpricipals | Get all users and groups in the current authentication schema. No parameters. |
| getrevisionanddoctype | Return the revision and doctype of a document. The output is String that looks like “rev;doctype”
|
| getversion | Get Metacat version. Return the current version of Metacat as XML. No parameters. |
| insert | Insert an XML document into the database. For an example, please see Inserting, Updating, and Deleting XML and Data Documents
|
| insertmultipart | Insert an XML document using multipart encoding into the database.
|
| isregistered | Check if an individual document exists in either the xml_documents or xml_revisions tables. For more information about Metacat’s database schema, please see the developer documentation.
|
| login | Log the user in. You must log in using this action before you can perform many of the actions. For an example of the login action, see Logging In.
|
| logout | Log the current user out and destroy the associated session. No parameters. |
| query | Perform a free text query. For an example, please see Searching Metacat.
|
| read | Get a document from the database and return it in the specified format. See Searching Metacat for an example.
|
| readinlinedata | Read inline data only.
|
| setaccess | Change access permissions for a user on a specified document.
|
| spatial_query | Perform a spatial query. These queries may include any of the queries supported by the WFS / WMS standards. For more information, see Spatial Queries.
|
| squery | Perform a structured query. For an example, please see Searching Metacat.
|
| update | Overwrite an XML document with a new one and give the new one the same docid but with the next revision number. For an example, please see Inserting, Updating, and Deleting XML and Data Documents.
|
| upload | Upload (insert or update) a data file into Metacat. Data files are stored on Metacat and may be in any format (binary or text), but they are all treated as if they were binary.
|
| validate | Validate a specified document against its DTD.
|
Metacat Replication Parameters
| Action | Description and Parameters |
|---|---|
| forcereplicate | Force the local server to get the specified document from the remote host.
|
| getall | Force the local server to check all known servers for updated documents. No parameters. |
| getcatalog | Send the contents of the xml_catalog table encoded in XML. No parameters. |
| getlock | Request a lock on the specified document.
|
| gettime | Return the local time on this server. No parameters. |
| servercontrol | Perform the specified replication control on the Replication daemon.
|
| read | Sends docid to the remote host.
|
| start | Start the Replication daemon with a time interval of deltaT.
|
| stop | Stop the Replication daemon. No parameters. |
| update | Send a list of all documents on the local server along with their revision numbers. No parameters. |
7.3.2. Logging In¶
To log in to Metacat, use the login action.
The following is an example of a Web form (see figure) that logs a user into Metact. Example HTML code is included below the screenshot.
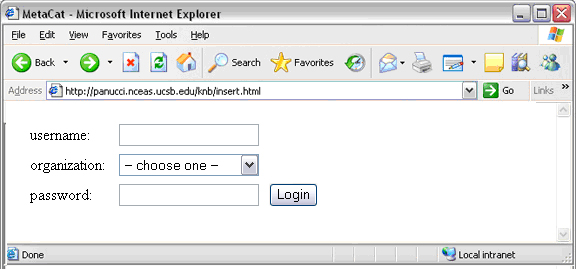
Logging into Metacat using an HTML form.
<html>
<body>
<form name="loginform" method="post"action="http://yourserver.com/yourcontext/servlet/metacat"
target="_top" onsubmit="return submitform(this);" id="loginform">
<input type="hidden" name="action" value="login"> <input type=
"hidden" name="username" value=""> <input type="hidden" name=
"qformat" value="xml"> <input type="hidden" name=
"enableediting" value="false">
<table>
<tr valign="middle">
<td align="left" valign="middle" class="text_plain">
username:</td>
<td width="173" align="left" class="text_plain" style=
"padding-top: 2px; padding-bottom: 2px;"><input name="uid"
type="text" style="width: 140px;" value=""></td>
</tr>
<tr valign="middle">
<td height="28" align="left" valign="middle" class=
"text_plain">organization:</td>
<td align="left" class="text_plain" style=
"padding-top: 2px; padding-bottom: 2px;"><select name=
"organization" style="width:140px;">
<option value="" selected>— choose one —</option>
<option value="NCEAS">NCEAS</option>
<option value="LTER">LTER</option>
<option value="UCNRS">UCNRS</option>
<option value="PISCO">PISCO</option>
<option value="OBFS">OBFS</option>
<option value="OSUBS">OSUBS</option>
<option value="SAEON">SAEON</option>
<option value="SANParks">SANParks</option>
<option value="SDSC">SDSC</option>
<option value="KU">KU</option>
<option value="unaffiliated">unaffiliated</option>
</select></td>
</tr>
<tr valign="middle">
<td width="85" align="left" valign="middle" class=
"text_plain">password:</td>
<td colspan="2" align="left" class="text_plain" style=
"padding-top: 2px; padding-bottom: 2px;">
<table width="100%" border="0" cellpadding="0"
cellspacing="0">
<tr>
<td width="150" align="left"><input name="password"
type="password" maxlength="50" style="width:140px;"
value=""></td>
<td align="center" class="buttonBG_login">
<input type="submit" name="loginAction" value="Login"
class="button_login"></td>
<td align="left"> </td>
</tr>
</table>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
7.3.3. Inserting, Updating, and Deleting XML and Data Documents¶
Adding, editing, and deleting XML documents in Metacat can be accomplished using the insert, update, and delete actions, respectively. Before you can insert, delete, or update documents, you must log in to Metacat using the login action. See Logging in for an example.
insert- Insert a new XML or data document into Metacat. You must specify a document ID.
update- Update an existing Metacat document. The original document is archived, then overwritten.
delete- Archive a document and move the pointer in xml_documents to xml_revisions, effectively “deleting” the document from public view, but preserving the revision for the revision history. No further updates will be allowed for the Metacat document that was “deleted”. All revisions of this identifier are no longer public.
Warning
It is not possible to “delete” one revision without “deleting” all revisions of a given identifier.
The following is an example of a Web form (see figure) that can perform all three tasks. Example HTML code is included in the sidebar.
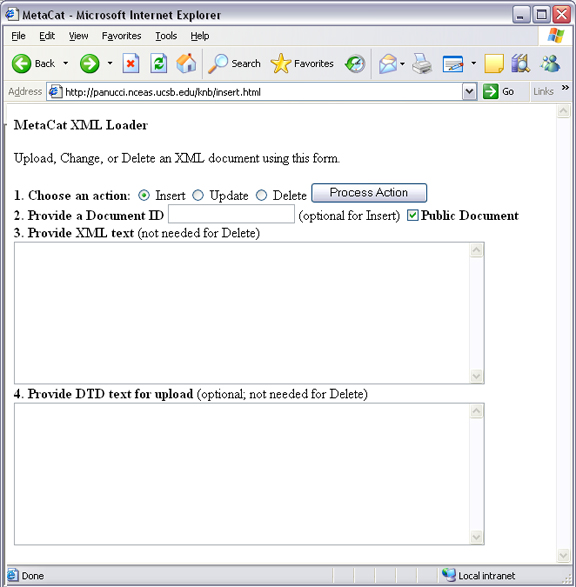
An example of a Web form used to insert, delete, or update XML documents in Metacat.
<html>
<head>
<title>MetaCat</title>
</head>
<body class="emlbody">
<b>MetaCat XML Loader</b>
<p>
Upload, Change, or Delete an XML document using this form.
</p>
<form action="http://yourserver.com/yourcontext/servlet/metacat" method="POST">
<strong>1. Choose an action: </strong>
<input type="radio" name="action" value="insert" checked> Insert
<input type="radio" name="action" value="update"> Update
<input type="radio" name="action" value="delete"> Delete
<input type="submit" value="Process Action">
<br />
<strong>2. Provide a Document ID </strong>
<input type="text" name="docid"> (optional for Insert)
<input type="checkbox" name="public" value="yes" checked><strong>Public Document</strong>
<br />
<strong>3. Provide XML text </strong> (not needed for Delete)<br/>
<textarea name="doctext" cols="65" rows="15"></textarea><br/>
<strong>4. Provide DTD text for upload </strong> (optional; not needed for Delete)
<textarea name="dtdtext" cols="65" rows="15"></textarea>
</form>
</body>
</html>
7.3.4. Searching Metacat¶
To search Metacat use the query or squery actions.
query:- Perform a free text query. Specify the returndoctype, qformat, returnfield, operator, searchmode, anyfield, and (optionally) a querytitle and doctype.
squery:- Perform a structured query by submitting an XML pathquery document to the Metacat server.
When Metacat receives a query via HTTP (screenshot below), the server creates a “pathquery” document, which is an XML document populated with the specified search criteria. The pathquery document is then translated into SQL statements that are executed against the database. Results are translated into an XML “resultset” document, which can be returned as XML or transformed into HTML and returned (specify which you would prefer with the returnfield parameter). You can also opt to submit a pathquery document directly, using an squery action.
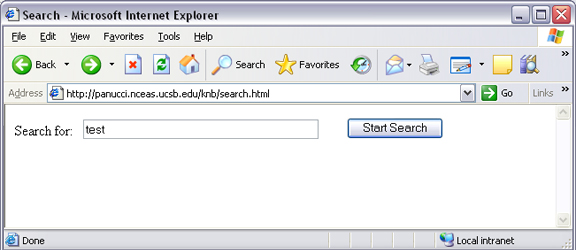
Example of a basic search form using a query action. The HTML code used to create the form is displayed below.
<html>
<head>
<title>Search</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="POST" action="http://panucci.nceas.ucsb.edu/metacat/metacat">
Search for:
<input name="action" value="query" type="hidden">
<input name="operator" value="INTERSECT" type="hidden">
<input name="anyfield" type="text" value=" " size="40">
<input name="qformat" value="html" type="hidden">
<input name="returnfield" value="creator/individualName/surName" type="hidden">
<input name="returnfield" value="creator/individualName/givenName" type="hidden">
<input name="returnfield" value="creator/organizationName" type="hidden">
<input name="returnfield" value="dataset/title" type="hidden">
<input name="returnfield" value="keyword" type="hidden">
<input name="returndoctype" value="eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.0.1" type="hidden">
<input value="Start Search" type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Metacat’s pathquery document can query specific fields of any XML document. The pathquery can also be used to specify which fields from each hit are returned and displayed in the search result set.
<pathquery version="1.0">
<meta_file_id>unspecified</meta_file_id>
<querytitle>unspecified</querytitle>
<returnfield>dataset/title</returnfield>
<returnfield>keyword</returnfield>
<returnfield>dataset/creator/individualName/surName</returnfield>
<returndoctype>eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.1.0</returndoctype>
<returndoctype>eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.0.1</returndoctype>
<returndoctype>eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.0.0</returndoctype>
<querygroup operator="UNION">
<queryterm casesensitive="true" searchmode="contains">
<value>Charismatic megafauna</value>
<pathexpr>dataset/title</pathexpr>
</queryterm>
<queryterm casesensitive="false" searchmode="starts-with">
<value>sea otter</value>
<pathexpr>keyword</pathexpr>
</queryterm>
<queryterm casesensitive="false" searchmode="contains">
<value>Enhydra</value>
<pathexpr>abstract/para</pathexpr>
</queryterm>
</querygroup>
</pathquery>
</pathquery>
Each <returnfield> parameter specifies a field that the database will
return (in addition to the fields Metacat returns by default) for each search
result.
The <returndoctype> field limits the type of returned documents
(eg, eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.0.1 and/or eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.0.0).
If no returndoctype element is specified, all document types are returned.
A <querygroup> creates an AND or an OR statement that applies to the
nested <queryterm> tags. The querygroup operator can be UNION or INTERSECT.
A <queryterm> defines the actual field (contained in <pathexpr> tags)
against which the query (contained in the <value> tags) is being performed.
The <pathexpr> can also contain a document type keyword contained in
<returndoc> tags. The specified document type applies only to documents
that are packaged together (e.g., a data set and its corresponding metadata file).
If Metacat identifies the search term in a packaged document, the servlet will
check to see if that document’s type matches the specified one. If not,
Metacat will check if one of the other documents in the package matches. If so,
Metacat will return the matching document. For more information about packages,
please see the developer documentation.
After Metacat has processed a Pathquery document, it returns a resultset document.
<resultset>
<query>
<pathquery version="1.0">
<meta_file_id>unspecified</meta_file_id>
<querytitle>unspecified</querytitle>
<returnfield>dataset/title</returnfield>
<returnfield>keyword</returnfield>
<returnfield>dataset/creator/individualName/surName</returnfield>
<returndoctype>eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.1.0</returndoctype>
<returndoctype>eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.0.1</returndoctype>
<returndoctype>eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.0.0</returndoctype>
<querygroup operator="UNION">
<queryterm casesensitive="true" searchmode="contains">
<value>Charismatic megafauna</value>
<pathexpr>dataset/title</pathexpr>
</queryterm>
<queryterm casesensitive="false" searchmode="starts-with">
<value>sea otter</value>
<pathexpr>keyword</pathexpr>
</queryterm>
<queryterm casesensitive="false" searchmode="contains">
<value>Enhydra</value>
<pathexpr>abstract/para</pathexpr>
</queryterm>
</querygroup>
</pathquery>
</query>
<document>
<docid>nrs.569.3</docid>
<docname>eml</docname>
<doctype>eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.0.0</doctype>
<createdate>2012-06-06</createdate>
<updatedate>2012-06-06</updatedate>
<param name="dataset/title">Marine Mammal slides</param>
<param name="creator/individualName/surName">Bancroft</param>
</document>
<document>
<docid>knb-lter-sbc.61.1</docid>
<docname>eml</docname>
<doctype>eml://ecoinformatics.org/eml-2.1.0</doctype>
<createdate>2012-06-06</createdate>
<updatedate>2012-06-06</updatedate>
<param name="dataset/creator/individualName/surName">Nelson</param>
<param name="dataset/creator/individualName/surName">Harrer</param>
<param name="dataset/creator/individualName/surName">Reed</param>
<param name="dataset/title">SBC LTER: Reef: Sightings of Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris) near Santa Barbara and Channel Islands, ongoing since 2007</param>
</document>
.....
</resultset>
When Metacat returns a resultset document, the servlet always includes the pathquery used to create it. The pathquery XML is contained in the <query> tag, the first element in the resultset.
Each XML document returned by the query is represented by a <document> tag. By
default, Metacat will return the docid, docname, doctype, doctitle, createdate
and updatedate for each search result. If the user specified additional return
fields in the pathquery using <returnfield> tags (e.g., dataset/title to return
the document title), the additional fields are returned in <param> tags.
Metacat can return the XML resultset to your client as either XML or HTML.
7.3.5. Paged Query Returns¶
Dividing large search result sets over a number of pages speeds load-time and makes the result sets more readable to users (Figure 4.12). To break your search results into pages, use the query action’s optional pagestart and pagesize parameters. The pagesize parameter indicates how many results should be returned for a given page. The pagestart parameter indicates which page you are currently viewing.
An example of paged search results.
When a paged query is performed, the query’s resultset contains four extra fields: pagestart, pagesize, nextpage, and previouspage (Figure 4.13). The nextpage and previouspage fields help Metacat generate navigational links in the rendered resultset using XSLT to transform the XML to HTML.
<!-- An example of an XML resultset that include support for page breaks.
The pagestart parameter will always indicate the page you are currently viewing.
-->
<resultset>
<pagestart>1</pagestart>
<pagesize>10</pagesize>
<nextpage>2</nextpage>
<previouspage>0</previouspage>
<query> ...</query>
<document>...</document>
<document>...</document>
</resultset>
The HTML search results displayed in the figure were rendered using Kepler’s XSLT, which can be found in lib/style/skins/kepler. Kepler’s XSLT uses the four extra resultset fields to render the “Next” and “Previous” links.
<a href="metacat?action=query&operator=INTERSECT&enableediting=false&anyfield=actor&qformat=kepler&pagestart=0&pagesize=10">Previous Page</a>
<a href="metacat?action=query&operator=INTERSECT&enableediting=false&anyfield=actor&qformat=kepler&pagestart=2&pagesize=10">Next Page</a>
In the example above, the current page is 1, and the previous page (page 0) and next page (page 2) pages are indicated by the values of the pagestart parameters.
7.3.6. Reading Data and Metadata¶
To read data or metadata from Metacat, use the read action. The read action
takes two parameters: docid, which specifies the document ID of the document
to return, and qformat, which specifies the return format for the document
(html or xml or the name of a configured style-set, e.g., default). If qformat
is set to xml, Metacat will return the XML document untransformed. If the
return format is set to html, Metacat will transform the XML document into
HTML using the default XSLT style sheet (specified in the Metacat
configuration). If the name of a style-set is specified, Metacat will use the
XSLT styles specified in the set to transform the XML.
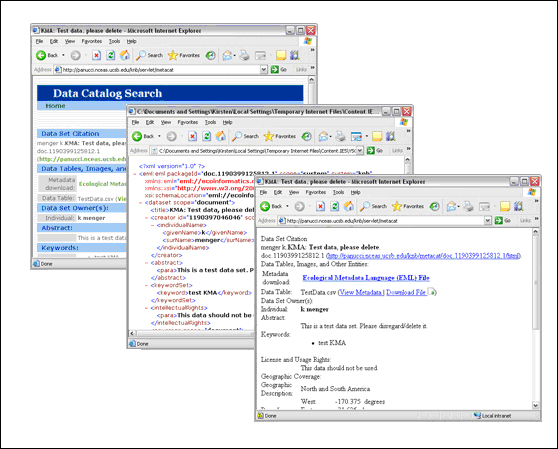
The same document displayed using different qformat parameters (from left to right: the default style-set, XML, and HTML).
Note that the read action can be used to read both data files and metadata files.
To read a data file, you could use the following request:
http://yourserver.com/yourcontext/metacat?action=read&docid=nceas.55&qformat=default
Where nceas.55 is the docid of the data file stored in the Metacat and
default is the name of the style (you could also use “html” or “xml” or the
name of a customized skin).
<html>
<head>
<title>Read Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="POST" action="http://your.server/your.context/servlet/metacat">
<input name="action" value="read" type="hidden">
<input name="docid" type="text" value="" size="40">
<input name="qformat" value="default" type="hidden">
<input value="Read" type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
7.4. Using the EarthGrid API (aka EcoGrid)¶
Note
The EarthGrid/EcoGrid web service API is deprecated as of Metacat 2.0.0 and will be removed from a future version of Metacat. Its functionality is being replaced by the standardized DataONE REST service interface. The EarthGrid API will be completely removed by the end of 2013.
The EarthGrid (aka EcoGrid) provides access to disparate data on different networks (e.g., KNB, GBIF, GEON) and storage systems (e.g., Metacat and SRB), allowing scientists access to a wide variety of data and analytic resources (e.g., data, metadata, analytic workflows and processors) networked at different sites and at different organizations via the internet.
Because Metacat supports the EarthGrid API (see table), it can query the distributed EarthGrid, retrieve metadata and data results, and write new and updated metadata and data back to the grid nodes.
For more information about each EarthGrid service and its WSDL file, navigate to the “services” page on your Metacat server (e.g., http://knb.ecoinformatics.org/metacat/services). Note that the AdminService and Version service that appear on this page are not part of EarthGrid.
EarthGrid/EcoGrid API Summary
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| AuthenticationQueryService | Search for and retrieve protected metadata and data from the EarthGrid as an authenticated user. Methods: |
| AuthenticationService | Log in and out of the EarthGrid Methods: |
| IdentifierService | List, lookup, validate, and add Life Science Identifiers (LSIDs) to the EarthGrid Methods: |
| PutService | Write metadata to the EarthGrid Methods: |
| QueryService | Search for and retrieve metadata from the EarthGrid Methods: |
| RegistryService | Add, update, remove, and search for registered EarthGrid services. Note: The WSDL for this service is found under http://ecogrid.ecoinformatics.org/registry/services Methods: |
7.5. Using Morpho¶
Morpho is a desktop tool created to facilitate the creation, storage, and retrieval of metadata. Morpho interfaces with any Metacat server, allowing users to upload, download, store, query and view relevant metadata and data using the network. Users can authorize the public or only selected colleagues to view their data files.
Morpho is part of the Knowledge Network for Biocomplexity (KNB), a national network intended to facilitate ecological and environmental research on biocomplexity. To use Morpho with your Metacat, set the Metacat URL in the Morpho Preferences to point to your Metacat server.
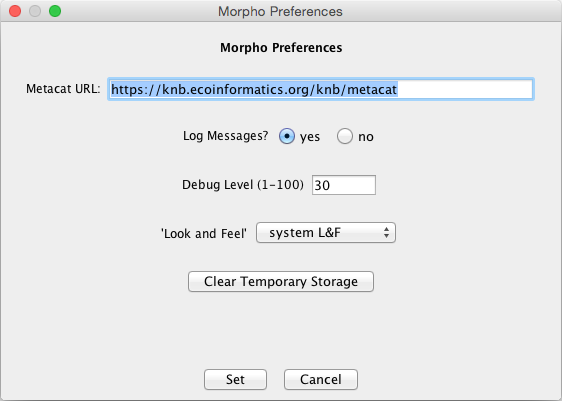
Set the Metacat URL in the Morpho preferences to point to your Metacat.
For more information about Morpho, please see: http://knb.ecoinformatics.org/
7.6. Creating Your Own Client¶
Note
NOTE: The Client API (and underlying servlet implementation) has been deprecated as of Metacat 2.0.0. Future development should utilize the DataONE REST service methods. The Client API will be completely removed by the end of 2013.
Metacat’s client API is available in Java and Perl (the Java interface is described in this section and further detailed in the appendix). Some of the API is also available in Python and Ruby. The API allows client applications to easily authenticate users and perform basic Metacat operations such as reading metadata and data files; inserting, updating, and deleting files; and searching for packages based on metadata matches.
The Client API is defined by the interface edu.ucsb.nceas.metacat.client.Metacat,
and all operations are fully defined in the javadoc documentation. To use the
client API, include the metacat-client.jar, utilities.jar, commons-io-2.0.jar, and
httpclient.jar in your classpath. After including these classes, you can
begin using the API methods (see the next table).
The following code block displays a typical session for reading a document from Metacat using the Java client API.
String metacatUrl = "http://foo.com/context/metacat";
String username = "uid=jones,o=NCEAS,dc=ecoinformatics,dc=org";
String password = "neverHarcodeAPasswordInCode";
try {
Metacat m = MetacatFactory.createMetacatConnection(metacatUrl);
m.login(username, password);
Reader r = m.read("testdocument.1.1");
// Do whatever you want with Reader r
} catch (MetacatAuthException mae) {
handleError("Authorization failed:\n" + mae.getMessage());
} catch (MetacatInaccessibleException mie) {
handleError("Metacat Inaccessible:\n" + mie.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
handleError("General exception:\n" + e.getMessage());
}
Operations provided by Client API (Metacat.java class)
| Method | Parameters and Throws | Description |
|---|---|---|
| delete | public String delete(String docid) throws InsufficientKarmaException, MetacatException, MetacatInaccessibleException; |
Delete an XML document in the repository. |
| getAllDocids | public Vector getAllDocids(String scope) throws MetacatException; |
Return a list of all docids that match a given scope. If scope is null, return all docids registered in the system. |
| getLastDocid | public String getLastDocid(String scope) throws MetacatException; |
Return the highest document ID for a given scope. Used by clients to determine the next free identifier in a sequence for a given scope. |
| getloggedinuserinfo | public String getloggedinuserinfo() throws MetacatInaccessibleException; |
Return the logged in user for this session. |
| getNewestDocRevision | public int getNewestDocRevision(String docId) throws MetacatException; |
Return the latest revision of specified the document from Metacat |
| getSessonId | public String getSessionId(); |
Return the session identifier for this session. |
| insert | public String insert(String docid, Reader xmlDocument, Reader schema) throws InsufficientKarmaException, MetacatException, IOException, MetacatInaccessibleException; |
Insert an XML document into the repository. |
| isRegistered | public boolean isRegistered(String docid) throws MetacatException; |
Return true if given docid is registered; false if not. |
| login | public String login(String username, String password) throws MetacatAuthException, MetacatInaccessibleException; |
Log in to a Metacat server. |
| logout | public String logout() throws MetacatInaccessibleException, MetacatException; |
Log out of a Metacat server. |
| query | public Reader query(Reader xmlQuery) throws MetacatInaccessibleException, IOException; |
Query the Metacat repository and return the result set as a Reader. |
| query | public Reader query(Reader xmlQuery, String qformat) throws MetacatInaccessibleException, IOException; |
Query the Metacat repository with the given metacat-compatible query format and return the result set as a Reader. |
| read | public Reader read(String docid) throws InsufficientKarmaException, MetacatInaccessibleException, DocumentNotFoundException, MetacatException; |
Read an XML document from the Metacat server. |
| readInlineData | public Reader readInlineData(String inlinedataid) throws InsufficientKarmaException, MetacatInaccessibleException, MetacatException; |
Read inline data from the Metacat server session. |
| setAccess | public String setAccess(String _docid, String _principal, String _permission, String _permType, String _permOrder ); throws InsufficientKarmaException, MetacatException, MetacatInaccessibleException; |
Set permissions for an XML document in the Metacat repository. |
| setMetacatUrl | public void setMetacatUrl(String metacatUrl); |
Set the MetacatUrl to which connections should be made. |
| setSessionId | public void setSessionId(String sessionId); |
Set the session identifier for this session. |
| update | public String update(String docid, Reader xmlDocument, Reader schema) throws InsufficientKarmaException, MetacatException, IOException, MetacatInaccessibleException; |
Update an XML document in the repository by providing a new version of the XML document. |
| upload | public String upload(String docid, File file) throws InsufficientKarmaException, MetacatException, IOException, MetacatInaccessibleException; |
Upload a data document into the repository. |
| upload | public String publicupload(String docid, String fileName, InputStream fileData, int size) throws InsufficientKarmaException, MetacatException, IOException, MetacatInaccessibleException; |
Upload a data document into the repository. |